The European Commission is working with the European automotive industry to build the critical mass of investment and engagement needed to maintain the EU industry’s competitive edge and leadership.
The EU’s automotive industry is facing several challenges: growing competition from non-EU manufacturers, car makers and tech companies, an increasing software complexity, the risks of dependence in supply chains, and a shortage of talents.
The EU’s automotive industry acknowledges these challenges and stakeholders are willing to collaborate for further developments in both automotive software and hardware:
- Regarding the software-defined vehicle (SDV), several alliances have been launched (ECLIPSE SDV working group, COVESA, AUTOSAR, SOAFEE, digital.auto, etc.). However, they lack a methodical system-level approach.
- Regarding digital automotive hardware, new open hardware architectures for automotive processors, including AI processors and chiplets are emerging. The EU could play a role in accelerating these developments and strengthening coordination.

Figure 1 - European Vehicle of the Future Initiative
Automotive software
The first stream of the initiative, the Software-defined vehicle of the future (SDVoF) ecosystem involves all major European automotive manufacturers and suppliers, and emphasises common, largely open-source building blocks, interfaces, and tools. Driven by a “code-first” approach, it promotes modular software based on open-source standards with improved maintainability, portability, and faster time-to-market.
Organisations participating in the FEDERATE and HAL4SDV consortia:
| Automotive OEMs | Automotive Tiers | SW development tool providers | Industry associations | Semiconductor companies | Academia & RTOs |
| BMW | Accenture | AVL | ANFIA | ARM | AGEN.EST.CON-SUP.INV-CIENT |
| Alkalee | Dassault | Astazero | |||
| Barcelona Supercomputing Center | |||||
| Daimler Truck | Bosch-ETAS | Eclipse Europe | AUTOSAR | CAE List | Commissariat à l'Énergie Atomique et aux Énergies Alternatives (CEA) |
| Continental - Elektro Bit | FEV | DLR | |||
| Fraunhofer-IKS | |||||
| Ford Otosan | Critical Software | Metis Baltic | COVESA | INFINEON | FZI |
| Dimecc | Teraglobus | INRIA | |||
| Instituto Superior Port | |||||
| Mercedez Benz | Forvia | Trustinsoft | EUCAR | NXP | KIT |
| Resiltech | Vector | Politecnico Di Milano | |||
| Politecnico Di Torino | |||||
| Renault-Ampere | Rovimatica | Verum | PFA | ST Microelectronics | RTWH Aachen |
| Sysgo GmbH | TU Berlin | ||||
| TU Eindhoven | |||||
| Stellatlantis | Tensor Embedded GmbH | VDA | TU Lulea | ||
| TTTech | TU Munich | ||||
| Univ. Ostrava | |||||
| Volvo Truck | Valeo | VDI/VDE-IT | Univ. Bologna | ||
| Vitesco | Univ. Côte d'Azur | ||||
| Univ. Stuttgart | |||||
| VW-Cariad | ZF | Univ. Oulu | |||
| Univ. Modena e Reggio Emilia | |||||
| VIV |
A governance structure has been established, with the major European automotive OEMs and suppliers steering the initiative. Participating companies have developed a Joint Roadmap and Vision document for the SDVoF ecosystem.
Several EU-funded actions have been launched in Horizon Europe, largely under the Chips Joint Undertaking of supporting joint developments and coordination. This includes the HAL4SDV project, which focuses on the hardware abstraction layer of the automotive software stack. Actions focusing on the middleware and API layer, on tools for SDVs enabling zero-emission mobility, and on in-vehicle electronic control architecture for connected and automated mobility are expected to be launched end of 2024.
Further actions are under consideration for the future. The FEDERATE coordination and support action orchestrates different research and innovation activities in the area, supports the governance of the initiative, and helps building a dynamic ecosystem.
Automotive hardware
Under the second stream of the initiative, the European Commission is promoting a broad pre-competitive collaboration on a RISC-V based automotive hardware platform, led by a coalition consisting of European integrated device manufacturers, research and technology organisations and upcoming start-ups/SMEs to deliver a next generation hardware architecture, including processors with AI computing capacity. This coalition has been working together on a joint roadmap, paving the way for future calls under the Chips Joint Undertaking. Further, it will focus on standardisation and collaboration to avoid duplication between efforts.
The roadmap is split into four key elements of RISC-V based processors:
- Scalable automotive real-time control processors
- High-performance application domain processors
- AI and machine learning accelerators
- System integration and interfacing, with particular emphasis on advanced packaging and heterogeneous integration.
In deploying these four elements together, the initiative aims to realise a comprehensive suite of processors and reference architectures for the automotive industry.
McKinsey & Company
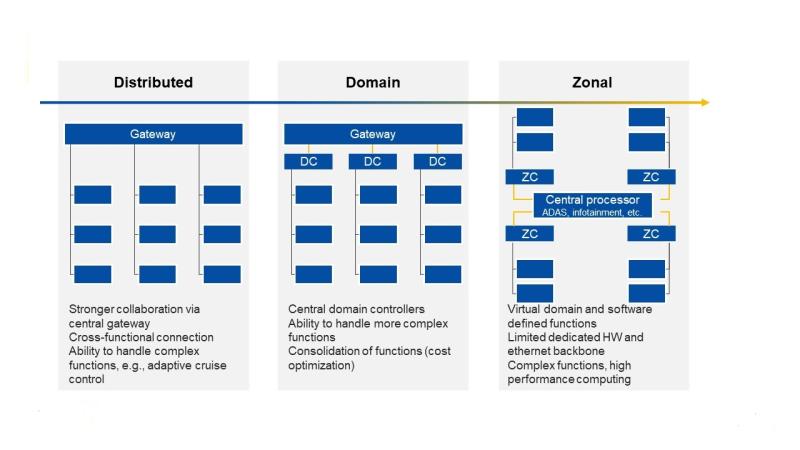
Figure 3 - Evolution of Electrical/Electronic (E/E) architecture towards next generation vehicles
Related Content
Big Picture
