The following projects all began under Horizon 2020. They include projects on the next generation Internet of Things, cloud computing, and software technologies. Further information on these projects can be found on the EUCloudEdgeIoT initiative's website.
Next generation Internet of Things projects
Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and applications have brought fundamental changes to all sectors of society and the economy. They constitute an essential element of the Next Generation Internet (NGI).
The challenge has been to leverage EU technological strength to develop the next generation of IoT devices and systems, which foster progress in enabling technologies such as 5G, cyber-security, distributed computing, artificial intelligence (AI), augmented reality and tactile internet.
The aim of the EU-funded research and innovation projects in this area has been to develop and demonstrate novel IoT concepts and solutions to underpin the vision of NGI in order to better serve the end-user.
The 6 selected projects of this topic, iNGENIOUS, IntelloT, IoT-NGIN, VEDLIoT, ASSIST-IoT and TERMINET, started at the end of 2020 and will run until the third quarter of 2023. They received €48 million in EU funding. The application take-up of these projects has been multiplied by the open calls amounting to almost €4 million. This further nurtures the creation of the ecosystem, where SMEs and industry actors are progressively integrated.
The Next Generation Internet of Things projects have generated great amount of scientific output by defining new architectures, machine learning methods and hardware integration aspects while considering cybersecurity and data privacy aspects.
Furthermore, the pilot projects tested the technologies in a great variety of domains, including: energy, environment, buildings, transport, mobility, logistics, industry, agriculture, food supply, crisis disaster management, health, smart cities, and communities.
View the call for these projects
Use Case: Pedestrian Automatic Emergency Breaking
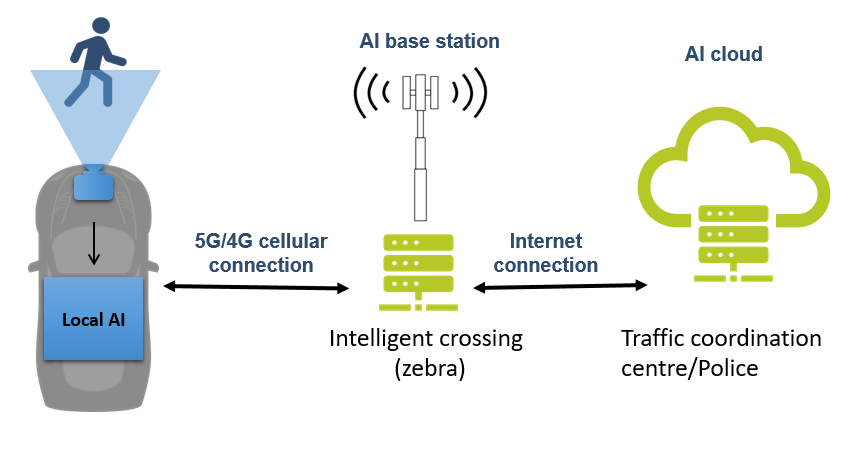
Horizon 2020: VEDLIoT project, EU contribution €8 million
The transport sector use case validates the deployment of pedestrian automatic emergency breaking. This system usesdata from IoT devices of the car, like cameras or sensors, and processes them onboard . The car communicates with the Intelligent Crossing, which processes the data and sends a control signal back to the car.
In case of potential collision, it would trigger the emergency braking system of the car. Different algorithms for urban and rural environments are still a challenge for future research, however the current achievements are already a great step forward to increasing pedestrian safety.
Use Case: Smart farming
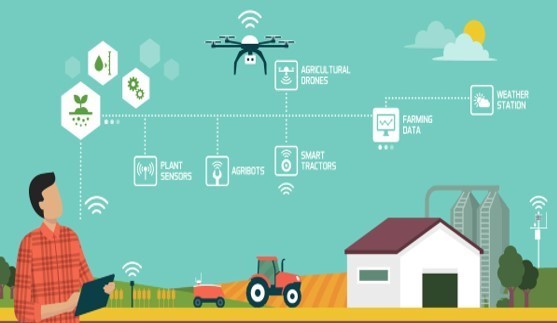
H2020 call project: TERMINET, EU contribution €8 million
Smart farming helps farmers to prevent damage to their crops. The system is based on data flows from Internet of Things (IoT) devices, like plant and livestock sensors, weather stations and farm facilities. Data from these devices is combined with periodically collected data, coming from drones and agribots.
The data flows to a local edge computing centre, which, in the case of agriculture, is the farm.
Some of this information is transferred to the cloud i.e. an agricultural app. The real time and daily information of the farm coupled with the cloud intelligence enables farmers to make qualified decisions. This way they can curb the damage to their crops, increasing yields, and, in turn, their profits. The environment is also benefiting from smart farming, as pesticide dosing will be more precise and its overall volume reduced.
Cloud computing: towards a smart cloud computing continuum projects
The challenge of research and innovation cloud computing projects is to develop comprehensive cloud solutions and testbeds, which combine various execution platforms for ubiquitous and seamless computing environments as a foundation for a complete computing continuum.
This requires novel solutions for federating infrastructures, programming applications and services, and composing dynamic workflows which can react in real-time to unpredictable data sizes, availability, locations and rates.
This will give application developers greater control over network, computing and data infrastructures and services. The end-user will also benefit from seamless access to continuous service environments.
The 5 selected projects PHYSICS, DATACLOUD, CHARITY , SERRANO and AI-SPRINT of this topic started at the beginning of 2021 and will run until the beginning of 2024. They received €19.4 million in EU funding.
Research and innovation in cloud computing has improved innovation in the field of cloud computing in Europe by creating new business models and increasing competitiveness of European industry, especially SMEs.
Research results have provided key technological building blocks for establishing an interoperable, open, secure and resource-efficient European Cloud infrastructure. The European industry has been empowered with novel tools and services to establish an alternative cloud offer, which allows European data to be stored and processed securely in Europe, according to European rules and values.
The European Cloud Federation will avoid market concentration around a few non-European players, which raises concerns for users over their ability to maintain the control over their data, and creates the risk of vendor lock-in.
View the call for these projects.
Software technologies projects
The increased complexity of present and emerging ICT systems poses several challenges at software and hardware level. This includes new requirements in terms of integration and cybersecurity. Users require seamless connectivity, abundant computing power and unlimited access to data, independently of the underlying infrastructure.
Therefore, we need to find new ways of managing this unprecedented complexity in software systems: from requirements analysis and design to development and testing, to deployment and operations across highly heterogeneous and dynamically self-reconfiguring systems.
The 7 selected projects of this topic COSMOS, ELEGANT, FOCETA, PIACERE, SWForum.eu, VeriDevOps and XANDAR started at the end of 2020 and will run until the fourth quarter of 2023. They received €30 million in EU funding.
Investments in software engineering impact the whole ICT domain because software is everywhere. All ICT technologies leverage software engineering tools. In particular, results from projects researching software technologies are impacting the way in which complex software systems are being developed such as cyber physical systems, safety critical systems, or services to be deployed on the cloud continuum.
The use and integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques in various phases of the software development and operation lifecycle, and the creation of novel toolchains embracing and extending the DevOps philosophy, have increased the efficiency and productivity of development teams. This is especially the case in SMEs.
In addition to the impact attained by the research and innovation project, SWForum has contributed with a research roadmap and policy recommendations in the domain of software engineering and open source.
The research efforts of the current H2020 projects in this area were reinforced by the coordination and support actions OPEN DEI , EU-IoT, SWForum and Hub4Cloud.
View the call for these projects
The following projects are funded under the Horizon Europe programme and began at the end of 2022 or the start of 2023. They include projects on meta operating systems and programming tools, cognitive cloud, and open source for cloud-based services. Further information on these projects can be found on the EUCloudEdgeIoT initiative's website.
Meta operating systems and programming tools for decentralised intelligence and swarms projects
In the previous framework programme, the European Union invested in centralised systems, with Internet of Things platforms hosted in central cloud locations. However, current research efforts are shifting to the new paradigm, which states that data processing needs to move from cloud to the edge and even to device level.
To enable and speed up this move, the Commission has launched 2 Horizon Europe calls for research and innovation actions for the edge-cloud continuum:
- Meta Operating Systems for the Edge;
- Programming tools for decentralised intelligence and swarms.
The first call aims to support research on meta operating systems for the Edge employing open platforms and promote an open edge ecosystem. Its goal is to orchestrate a large number of distributed heterogenous computing resources.
The 6 selected projects of this topic, NEPHELE, ICOS, AeROS, NEMO, NebulOus and FluidOS, started at the end of 2022 and will run until 2025. They will receive €59 million in EU funding.
The second call focuses on research and innovation for programming tools for decentralised intelligence and swarms. The projects are developing agile and secure architectures for collaborative smart nodes, with decentralised or swarm intelligence and autonomy. The 5 selected projects of this topic, OpenSwarn, INCODE, SMARTEDGE, TaRDIS and OASEES, started at the beginning of 2023 and will run until 2025. They will receive €37 million in EU funding.
Both sets of projects aim to improve energy efficiency, build trustworthy and secure open-source solutions, and support open standards. They are based on AI, compliant to the data space principles and explore advanced concepts, such as self-optimisation, self-healing and reconfiguration.
To facilitate the uptake of their solutions, the projects will demonstrate the meta operating systems and swarm technologies in key sectors such as energy, transport, mobility, agriculture, farming, health, logistics, manufacturing, factories, buildings, utilities, smart cities and communities.
View the call for meta operating systems
View the call for decentralised intelligence and swarms
Use case: Edge computing containers near renewable energy sources
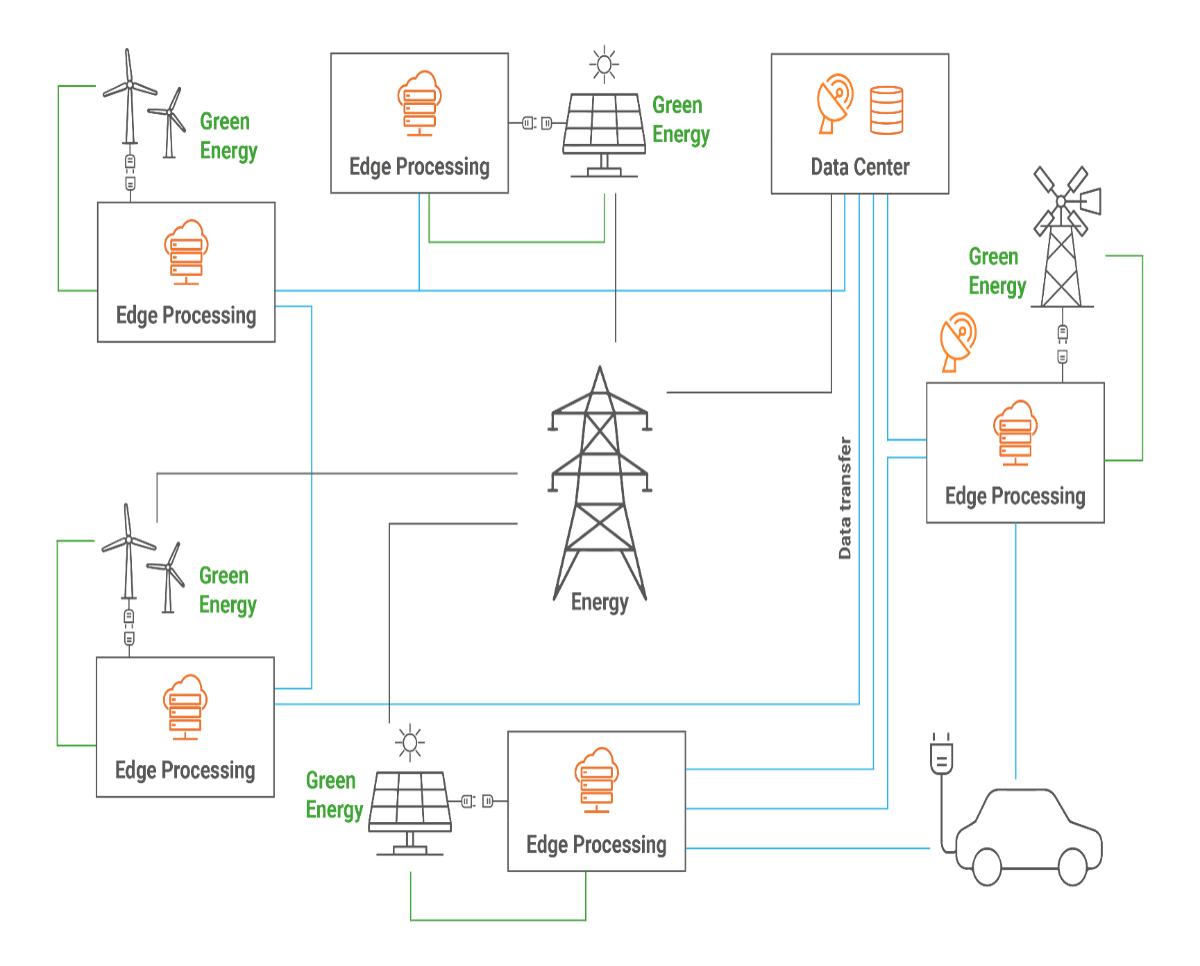
Horizon Europe: AEROS project, EU contribution €12 million
Given the application of meta operating systems in the energy domain, data flows from IoT devices of the wind and photovoltaic sources, to edge computing nodes located directly at energy sources and connected to them.
The nodes process the data and send it back to the energy sources. They also send and receive aggregated data to and from the cloud. Coupled with cloud intelligence, energy providers can make coordinated decisions to balance the electricity network. Orchestration of the energy production of wind and photovoltaic energy leads to more optimal consumption and increased profits for energy providers.
Use case: Smart logistics at terminal stations
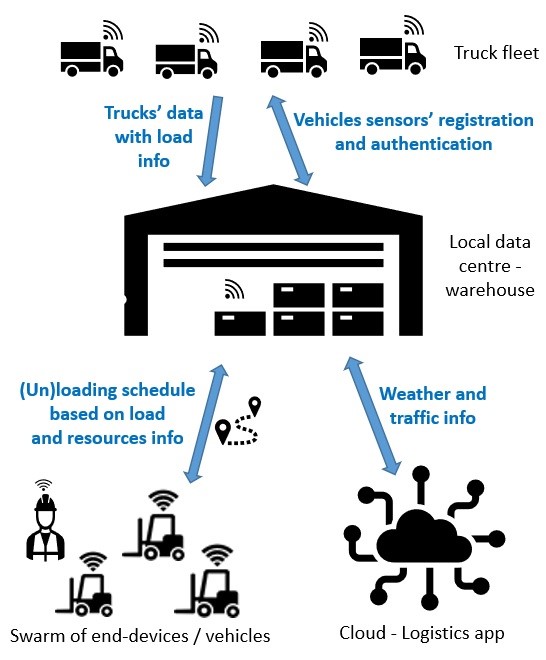
Horizon Europe: INCODE project, EU contribution €8 million
In the example of the use case in the logistics sector, swarm technology brings economic, safety and legal benefits.
The load information, including the transport conditions of items such as perishable food, flows from mobile IoT sensors of the truck fleet in real time to the local data centre at the warehouse. Here, it is used to register and authenticate the shipment.
Static IoT sensors in the warehouse provide inventory status information. Some of the local data is combined with cloud intelligence via a logistics app. Then the local data centre receives commands to manage a swarm of end-devices/vehicles for (un)loading of the trucks according to a schedule.
This prevents damage to perishables and reduces of the unit costs of using trucks and loading vehicles. Coordinated (un)loading also provides benefits in terms of work safety as it prevents product mishandling.
Moreover, the logistics app is a trusted legal framework for all the logistics actors: road carriers, customs, warehouses, distributors, even retailers.
Cognitive cloud: AI-enabled computing continuum from cloud to edge projects
Artificial Intelligence will transform current clouds into cognitive clouds. Cognitive clouds will interact with all the layers in the computing continuum and respond and adapt intelligently to changes in application behaviour and data variability. It will offer automatic deployment, and mobility and adaptability of services from cloud to edge.
Application developers will be empowered by greater control over network, computing and data infrastructures and services, and the end-user will benefit from seamless access to a continuous service environment.
From the HE WP2021-22 call on Cognitive Cloud: AI-enabled computing continuum from Cloud to Edge (HORIZON-CL4-2022-DATA-01-02), 9 research and innovation projects were selected: AC3; ACES; CloudSkin; CODECO; COGNIFOG; DECICE; EDGELESS; MLSysOps; SovereignEdge.Cognit. The projects started at the beginning of 2023 and will run until the end of 2025. They will receive €50 million in EU funding.
View the call for cognitive cloud projects
Open source for cloud-based services projects
Open source for cloud-based services projects develop virtual environments, methods and tools. These can work with the deployment of full open source stacks from the kernel to cloud applications, featuring targeted relevant processing architectures of European initiatives. For example, RISC-V.
Required developments provide a simulation of the targeted architecture that allows validation, verification and testing of the trustworthiness of software layers over specific architectures.
Open hardware interfaces are able to integrate components in processor architectures, and are prepared for deploying cloud applications. The focus should be optimising and expanding the interface possibilities of the aforementioned components, in regards to existing hardware computing standards.
Software should provide the basic initialisation of cloud servers based on processor components and the runtime interfaces for operating systems and programs.
The 4 selected research and innovation projects of this topic, AERO; OpenCUBE; RISER and Vitamin-V, started at the beginning of 2023 and will run until the end of 2025. They will receive €22 million in EU funding.
The research efforts of the recently started projects are reinforced by the coordination and support actions OpenContinuum and Unlock-CEI. The amount of EU funding for these 2 actions is €3 million. They started in mid-2022 and will run until the end of 2024.
Furthermore, coordination and support action on the Roadmap for next generation computing and systems technologies, has been selected for financing under dedicated topic – HiPEAC. The amount of EU funding allocated to HiPEAC is €2 million. The action started in late 2022 and will run until mid-2025.
View the call for open source projects
View the call for the roadmap support action
The following calls have either recently closed and are awaiting decisions, or will be opening later this year.
Cognitive computing continuum: Intelligence and automation for more efficient data processing call
Projects of this call topic are expected to contribute to the following outcomes:
- Enhancing openness and open strategic autonomy in the evolving data and AI-economies across the computing continuum, including adapted system integration at the edge and at device level, validation of key sectors and nurturing European value chains to accelerate and steer the digital and green transitions.
- Paving the way to strategic industrial cooperation in data processing required to support future hyper-distributed applications, by building open platforms underpinning an emerging industrial open edge ecosystem, which is critical to establishing a mature European supply chain.
- Establishing adaptive hybrid computing, cognitive clouds and edge intelligence beyond today’s investments on data infrastructure.
The research and innovation projects of this topic were selected in 2023 and are expected to start at the beginning of 2024 and run until the end of 2026.
Projects covering this topic will receive €28 million in EU funding.
The research efforts of the selected projects will be reinforced by the coordination and support action focused on Computing Continuum research and policy. This action will be allocated an amount of €2 million in EU funding.
Furthermore, coordination and support action on the collaboration with the National Science Foundation (NSF) on fundamental research and on new concepts for distributed computing and swarm intelligence, will be selected for financing. This action will be allocated an amount of €1 million in EU funding.
View the call for the cognitive computing continuum
View the call for the support action for cloud computing continuum research and policy
View the call for the collaboration with NSF
Piloting emerging Smart IoT Platforms and decentralised intelligence call
This call topic is planned to be opened at the end of 2023. It is expected to contribute to the implementation of edge paradigms in real environments, and pave the way to strategic industrial cooperation in data processing. This is necessary to support future hyper-distributed applications by building European supply chains, underpinning an emerging open edge ecosystem, demonstrating cross-domain standardisation and up-scaling edge infrastructure solutions.
The selected innovation projects are expected to start at the beginning of 2025 and will run until the end of 2027.The amount of €45 million in EU funding will be allocated to the projects covering this topic.
View the call for smart IoT platforms
Open Source for Cloud/Edge to support European Digital Autonomy call
This call will open in late 2023. It is expected to contribute to both of the following outcomes:
- Demonstrating prototypes of cloud and edge servers in relevant centralised and distributed environments and allowing full computing infrastructure deployments, based on European processor technology. This should thereby establish a full Open Computing Architecture stack, which supports emerging processing architectures, such as RISC-V.
- Consolidating standards and best practices of the European Open Computing Architecture, and considering how it adapts to current industry standards.
The selected research and innovation projects are expected to start at the beginning of 2025 and will run until the end of 2027. The amount of €20 million in EU funding will be allocated to the projects covering this topic.
Projects of this topic will be supported by the coordination and support action on a public recognition scheme for open source. This action will be allocated €2 million in EU funding.
View the call on open source for cloud/edge to support European Digital Autonomy
View the coordination and support action on a public recognition scheme for open source
Fundamentals of Software Engineering call
This call topic will open in late 2023. It is expected to contribute to the development of responsible software engineering methods, tools, and best practices. It will leverage, among other things, novel AI and data technologies to accelerate the development and maintenance of software. This includes multi-architecture systems, addressing in particular efficient and agile modelling, verification and validation, and vulnerability assessment and mitigation.
The selected projects are expected to start at the beginning of 2025 and will run until the end of 2027. The amount of €14 million in EU funding will be allocated to the projects covering this topic.
The research efforts of these projects will be supported by the coordination and support action on a public recognition scheme for open source. This action will be allocated €2 million in EU funding.
View the call on the fundamentals of software engineering
View the coordination and support action on a public recognition scheme for open source
Calls of 2025 to 2027 in the making
The Directorate-General for Communications Networks Content and Technology (DG CNECT) organised a meeting on “Concertation and Consultation on the Computing Continuum: From Cloud to Edge to IoT” on 10-11 May 2023. Besides the concentration activities of the projects, the aim was to discuss the research priorities for 2025-2027 with experts in the field.
The event brought together organisations and individuals from different communities to present their expression of interest in the area of Cloud, Edge and IoT. Stimulating discussion among the experts facilitated by DG CNECT has generated a wealth of intelligence, which will feed into Commission’s future definition of research areas for investments.
The participants of the Consultation part of the event identified a European vision for the cloud-edge-IoT domain with 4 main research directions for the next Horizon Europe Work Programme (2025-2027). These research directions were presented in the wrap-up session at the end of the day and received strong support from the participants:
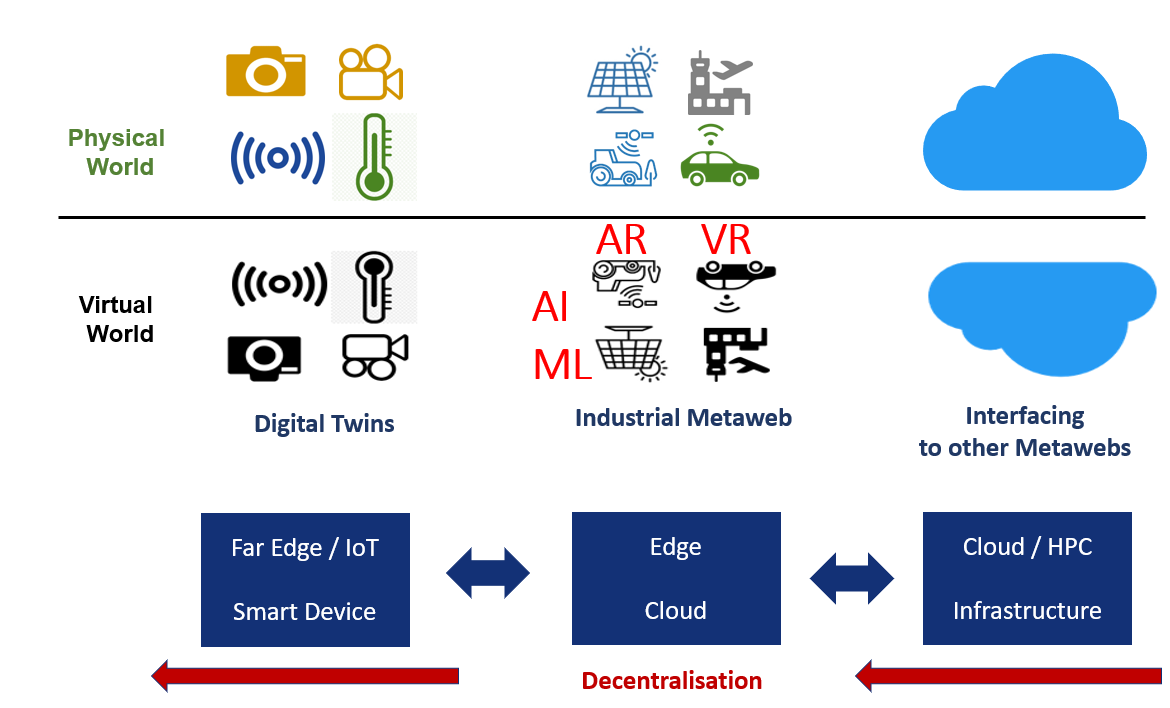
The 4 research directions
- Computing Continuum Infrastructure/EU Cloud Servers
A transformation of the Computing Continuum Infrastructure is required, particularly in relation to European Cloud-Edge Servers. Digital autonomy in the Computing Continuum is only achievable with a strategic intervention that leads to a paradigm shift. The adoption of RISC-V, an open-source Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), is widely proposed and supported as the only means to strengthen EU sovereignty in the Computing Continuum. Following EU investments in processors for HPC, the next step would be a cloud-edge server market. The importance of energy-aware computing and the creation of federated catalogues for effective resource sharing is also to be considered in line with foreseen Cognitive Cloud-Edge Continuum developments.
- Cognitive Cloud-Edge Continuum
This section discussed and identified key challenges for the cloud to edge continuum imposed by the new emerging trends like virtual worlds. To make the industrial metaverse and virtual worlds become reality, the digital and physical strands of a defined space need to be woven together into the fabric of a new universe that is orchestrated by an intelligent cloud to edge to IoT continuum.
There is a need for end-to-end intelligent enablement for the orchestration of the data, computing, and AI capacity across the cloud-to-edge/IoT continuum. This should lead to trustworthy decision making for business and private users. It presents several research challenges including end-to-end AI integration, dynamic data orchestration, new runtime management of the continuum, self-adapting clouds, decentralised optimisation and convergence with 5G/6G.
- Next Generation MetaOS for IoT-Edge
This part identified challenges stemming from merging the physical and virtual world. Driven by the widespread use of IoT objects and connected systems, the complexity of data handling at the edge is characterised by data inflation, heterogeneity of data types, and task concurrency. This complexity emphasises the role of emerging network functions, a transition from internet of things to internet of digital twins, from cloud and central computing to spatial computing. This also brings benefits from advanced technologies like extended reality (XR), going beyond system automation and robotics towards the vision of an industrial metaverse.
Claiming that the industrial metaverse is more mature than the consumer-driven metaverse, emphasis was put also on the importance of distributed intelligence and collaborative industrial systems at the IoT-Edge Continuum as part of broader Cloud-Edge Continuum challenges.
- Cybersecurity, Privacy, Interoperability, Open Source and Software Engineering:
The final section discusses the challenges of secure SecDevOps for complex systems, using AI for all phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and Service Operation Life Cycle (SOLC). It also highlights the importance of managing security in the software supply chain and ensuring data confidentiality in the cloud-edge continuum. The section concludes with a discussion on new software engineering mechanisms for the development of (hybrid) quantum software and the importance of open hardware and software.
Read more about the event
Read a summary of the Concertation Day (.pdf)
Read a summary of the Consultation Day (.pdf)