The future Internet of Things and Edge Computing can revolutionise the way production and processes are organised and monitored across strategic value chains.
Along with artificial intelligence (AI) and big data, the Internet of Things (IoT) is at the centre of the digitisation of the world economy. Data collected from sensors can be monitored and fed back to instigate an action, gain insights or respond to another connected object hundreds of miles away. With processing moving to the edge, we can avoid unnecessary communication and storage costs whilst applying machine learning and AI to identify data patterns that have an impact on physical processes or businesses.
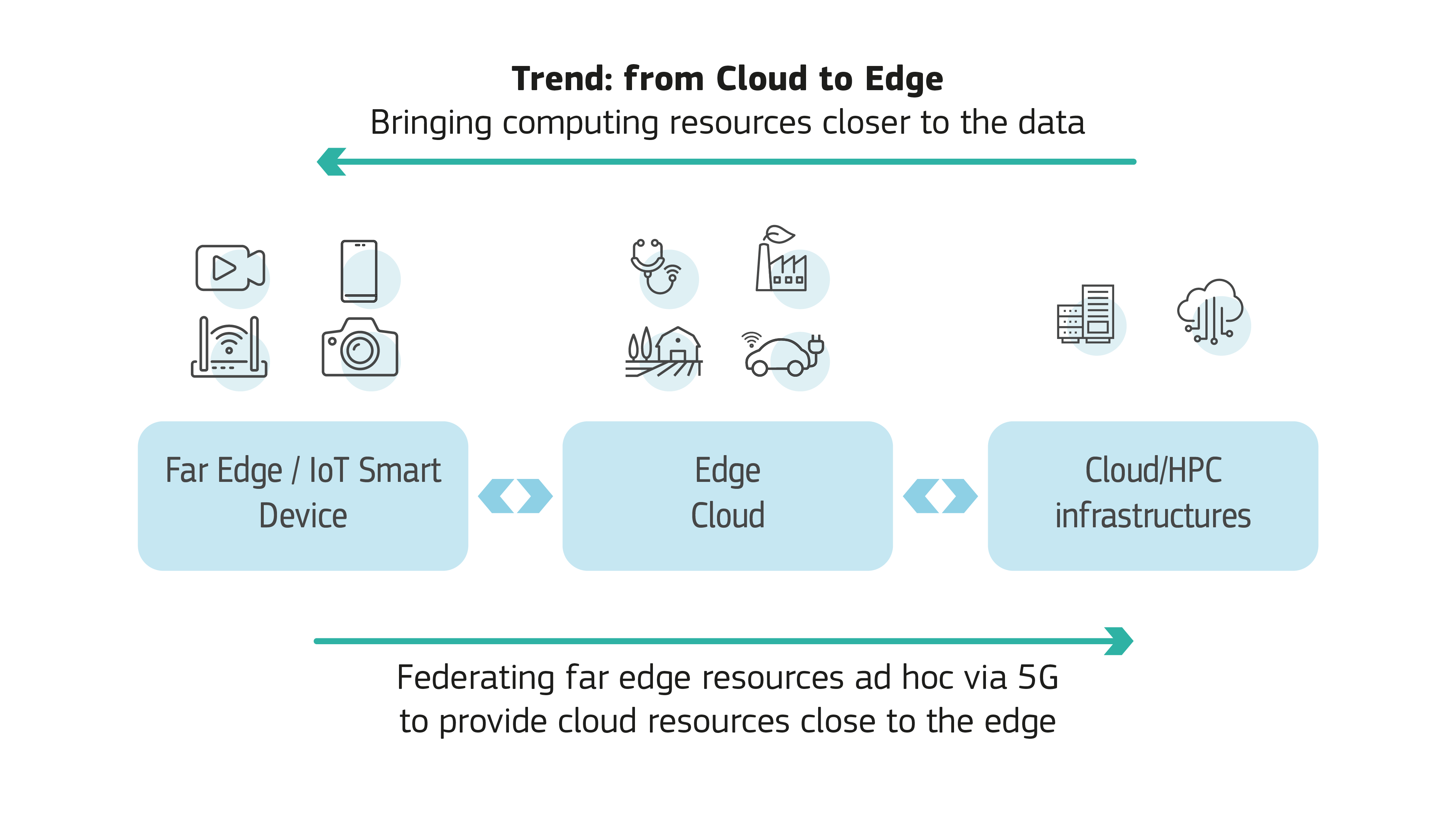
Figure 1: Cloud-Edge-IoT Orchestration
Considering the exponential growth of connected devices and systems, data processing and analytics are becoming the engine for the digitisation of our economy, society and environment. With devices becoming ever smarter in collecting data, processing and transmitting information, and triggering actions in real-time, the IoT is at the heart of this digital transformation, integrating devices, data, computing power and connectivity.
The future Internet of Things
The IoT creates smart environments with digital technologies to optimise the way we live our lives. The rollout of over 41 billion IoT devices is expected by 2025 (International Data Corporation). This will lead to an exponential growth of data and push computing operations and data analytics to the edge.
Edge computing builds on a multi-layer technology that enables the management, and automation of connected IoT devices. It is the logical evolution of the dominant cloud computing model, avoiding the transfer of mission-critical data to the cloud, supporting resilience, real-time operations, and security, privacy and protection. At the same time, it reduces energy consumption and our carbon footprint. In edge computing, the processing moves from a centralised point, closer to (or even into) the IoT device itself: the 'edge' or periphery of a network.
The research, innovation and deployment of the next generation of IoT will need a strong computing capacity at the edge in order to support Europe’s digital autonomy in future ICT systems. This will be achieved by creating a computing continuum – from swarms of far edge devices to the cloud – and involves smart platform building driven by key European players.
Europe’s IoT strategy
As the starting point for discussions on a next generation IoT strategy, the Next Generation Internet of Things (NGIoT) project carried out a workshop in September 2020 on Cloud-to-Edge-to-IoT, which addressed the technology challenges and competitive impact for European stakeholders in light of their role in a data economy.
In March 2021, the Commission’s Fireside Chat workshop mobilised a small number of expert stakeholders from sectors such as aerospace, agriculture, automotive, construction machinery, home and industrial automation, with the aim of designing a European strategy for future IoT and edge computing, with a market window of over 5 years.
A general consensus was reached, even between competitors, on the need for trusted IoT and edge computing platforms and orchestration mechanisms to support the next stage of digitisation. Industrial actors welcomed the Commission’s initiative to provide R&I support under Horizon Europe, bridging the joint undertakings on key digital technologies and smart networks and services; the partnership on AI, data and robotics; and adoption-oriented initiatives on sectoral data spaces and cloud-edge federations.
In April 2021, following on from the Fireside Chat, the NGIoT & Edge Computing Strategy Forum – co-organised by the Commission with the EU-IoT project – gathered technology experts from various digital and vertical domains to exchange views on the priorities, challenges and opportunities ahead.
The forum also established a commonly shared strategic vision for the next-generation IoT and (far) edge computing in Europe. It welcomed over 30 speakers and 300 attendees over 14 plenary sessions on system ecosystems and alliances, integration platforms, trustworthiness, and visionary concepts, sparking insightful discussions throughout the event.
EU funding programmes
Horizon Europe: Following from the success of Horizon 2020, Horizon Europe will contribute more than €150 million into R&I under its 2021-22 Calls on 'World Leading Data and Computing Technologies: From Cloud to Edge to IoT for European Data', supporting the trend to the edge with the development and deployment of next generation computing components, systems and platforms. This will enable the transition to a computing continuum with strong capacities at the far edge in an energy-efficient and trustworthy manner.
Under Horizon Europe’s Cluster 4 Destination 3, the Commission selected a group of projects on the next generation of meta-operating systems to provide value in key industrial and societal applications, such as buildings, automotive, agriculture and energy, all of which will require more computing power at the edge in the years to come. Receiving €64 million in EU funding and with the goal of building a European IoT and edge ecosystem, 6 research and innovation actions – ICOS, FluiDOS, NEMO, NebulOus, aeROS and NEPHELE – and 3 coordination and support actions – OpenContinuum, Unlock-CEI and HiPEAC – will support the emergence of such an open ecosystem by publishing open calls on the new eucloudedgeiot.eu web portal, particularly targeting midcaps, SMEs and start-ups. The cluster was announced during the “Future European Platforms for the IoT and the Edge” session at the June 2022 edition of IoT Week in Dublin and will launch on 1 September, with Unlock-CEI and HiPEAC launching on 1 June and 1 December respectively.
In other areas of the programme like Cluster 2: Culture, Creativity and Inclusive Society, IoT is addressed as a critical enabler for attaining the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals and the goals of the European Green Deal. For example, industrial digitisation presents opportunities for distance-monitoring of air and water pollution, optimising how energy and natural resources are used, and how responsible operations are performed across the aforementioned vertical sectors.
Digital Europe: In addition to Horizon Europe, the Commission’s Digital Europe programme (DIGITAL) will bring data and cloud services to EU businesses, citizens and public administrations, aiming to set up common European data spaces in different vertical sectors such as agricultural, mobility and energy, complemented by a trustworthy, energy-efficient cloud infrastructure. In April 2021, the Open DEI project published a position paper underlining the importance of such data spaces in creating a future data economy through the sovereign sharing of data, not only within sectors but also across them.
DIGITAL will also strengthen existing AI testing and experimentation facilities (TEFs) in areas like healthcare and mobility, and subsidise European digital innovation hubs in order to boost the digitisation of SMEs and help European companies to become more competitive in the digital age.
These new initiatives are building on the successes of Horizon 2020. The Digitising European Industry (DEI) area prioritises ecosystem building, platform interoperability, technology integration, standardisation and validation through large-scale pilots and TEFs. It focuses on the following key sectors: agriculture, energy, manufacturing, mobility, healthcare and smart communities.
The EU supports the development of industrial IoT platforms, essential for the integration of key digital technologies in real-world applications, processes, products and services. Complementing various policy initiatives, the Commission made available around €400 million through its Horizon 2020 programme for efforts on platform building and large-scale piloting under the DEI focus area. Some of these projects have already finished or are coming to an end, while others are just launching and will continue running into 2023.
Cross-domain collaboration
The Alliance for IoT and Edge Computing Innovation (AIOTI) was initiated by the Commission to support the creation of a European industry-driven IoT ecosystem. To better understand this ecosystem, a study in June 2019 investigated the landscape of physical and virtual clusters of enterprises, research organisations and academia working on the development and market deployment of IoT technologies and applications.
The Advanced Research & Technology for Embedded Intelligent Systems Industry Association (ARTEMIS-IA) represents members in European industry, SMEs, universities and research institutes in the Electronic Components & Systems for European Leadership Joint Undertaking (ECSEL-JU). ARTEMIS-IA promotes the research and innovation interests of its members to the Commission as well as to the governments of participating Member States.
Latest News
Ábhar Gaolmhar
An Pictiúr Mór
The EU actively cooperates with industry, organisations and academia to unleash the potential of the Internet of Things across Europe and beyond.
Léargas níos doimhne
Tá líon mór píolótaí nuálaíochta ar conradh ag an gCoimisiún chun cuidiú le digitiú na tionsclaíochta, lena n-áirítear earnáil an chúraim sláinte, a chur chun cinn.
Le blianta beaga anuas, tá roinnt mhaith píolótaí mórscála bunaithe ag an gCoimisiún chun cuidiú le digitiú na tionsclaíochta a chur chun cinn ar fud na hEorpa agus níos faide i gcéin.
Féach freisin
Leagtar amach i gclár beartais an Aontais Eorpaigh maidir le Deich mBliana Digiteacha na spriocanna atá againn don chlaochlú digiteach, agus tá 10,000 imeall-nód neodrach ó thaobh na haeráide de mar sprioc amháin. Ciallaíonn sé seo go bhfuil ról mór le himirt ag scamall, imeall...
D’fhéadfadh digitiú earnáil talmhaíochta na hEorpa athrú ó bhonn a dhéanamh ar an tionscal, agus éifeachtúlacht, inbhuanaitheacht agus iomaíochas á gcur chun cinn.
Find out more
Industrial platforms and large-scale pilots
Digital industrial platforms are key to placing Europe ahead in the digital transformation, linking...
Data solutions for energy: from mobility to home and appliances
The Commission has established numerous large-scale pilots to help drive the digitisation of...
